An LED display screen is a type of electronic display that utilizes light-emitting diodes (LEDs) as the primary source of light to create images and videos. These screens are widely used in televisions, computer monitors, billboards, digital signage, and stadium scoreboards due to their superior brightness, energy efficiency, and longevity. Unlike traditional LCD screens that require a separate backlight, LED screens generate their own illumination, allowing for higher contrast, better color reproduction, and improved visibility in both indoor and outdoor environments. LED display screens can be configured in various sizes and resolutions, making them suitable for applications ranging from small advertising panels to massive video walls used in concerts and sports events. Their fast response time and high refresh rates ensure smooth visuals, making them ideal for displaying dynamic content.
An LED screen is composed of several essential components, including LED modules, driver circuits, power supply units, a control system, and a protective outer casing. The LED modules contain an array of tiny light-emitting diodes, typically in red, green, and blue (RGB) colors, which blend to produce a full spectrum of colors. These modules are arranged in a grid pattern to form pixels, determining the display's resolution and clarity. The driver circuit manages the electrical current supplied to the LEDs, ensuring precise brightness and color adjustments for accurate image reproduction. A power supply unit converts electrical input into the required voltage and current levels for stable operation. The control system processes video signals, transmitting data to the LEDs to display content seamlessly. Additionally, the screen is enclosed in a durable, weather-resistant casing that protects it from environmental factors such as dust, moisture, and physical damage, especially for outdoor applications.
(1)Basic Structure of an LED Screen
An LED screen consists of three primary components:
LED Pixels: Each pixel is made up of three tiny LEDs—Red, Green, and Blue (RGB). By adjusting the brightness of these LEDs, different colors are created.
Driver Circuit: Controls the voltage and current sent to each LED to adjust brightness and color.
Display Controller: Processes video signals and determines how the LEDs should be lit to form an image.
(2)How Images Are Formed
An LED screen creates images by combining tiny red, green, and blue (RGB) LEDs to produce different colors. Each pixel on the screen consists of these three LEDs, and by adjusting their brightness levels, the screen can generate millions of colors. When viewed from a distance, these individual LEDs blend to form a seamless image. The screen's resolution depends on the number of pixels, with higher resolutions offering sharper and more detailed visuals.
To display images or videos, the LED screen rapidly updates pixel colors in response to incoming signals. This process, known as the refresh rate, ensures smooth motion and fluid transitions between frames. Modern LED screens have high refresh rates, minimizing flickering and improving image clarity, especially for fast-moving visuals like sports or gaming. Additionally, LED screens use precise color calibration to maintain consistent and accurate color representation, making them ideal for both indoor and outdoor displays.
LED screens offer several advantages, making them a popular choice for various applications, from televisions and smartphones to large digital billboards. One of the key benefits of LED screens is their high brightness and clarity. Unlike traditional LCD screens that rely on a backlight, LEDs emit their own light, allowing for superior brightness levels. This makes LED screens highly visible even in bright outdoor environments, ensuring that images and videos remain sharp and vibrant under different lighting conditions.
Another major advantage of LED screens is their energy efficiency and long lifespan. LEDs consume significantly less power compared to traditional display technologies such as incandescent or fluorescent lighting. This not only reduces electricity costs but also makes LED screens a more environmentally friendly option. Additionally, LEDs have a longer operational lifespan, often lasting tens of thousands of hours before needing replacement. This durability reduces maintenance costs and ensures long-term reliability, making LED screens a cost-effective investment.
LED screens also offer superior response times and refresh rates, leading to smoother motion and reduced lag in videos. This makes them ideal for applications that require fast-moving visuals, such as gaming, sports broadcasts, and digital advertising. Unlike older technologies, LED screens can quickly adjust brightness and color, minimizing motion blur and flickering. Their ability to produce deep blacks and vibrant colors enhances overall image quality, making them the preferred choice for modern displays across various industries.
Brightness and Contrast
One of the biggest differences between LED and LCD screens is the quality of brightness and contrast. LED screens, due to their superior backlighting technology, offer significantly brighter images compared to traditional LCDs. This makes them ideal for use in bright rooms or environments where the screen needs to stand out even under ambient light.
In addition to brightness, LED screens generally have superior contrast ratios. Since LEDs can be individually controlled in more advanced setups (such as OLED or full-array LED displays), they can produce deeper blacks, leading to better contrast. Traditional LCDs, with their fluorescent backlighting, often struggle to achieve true black levels, leading to grayer dark scenes.
Color Accuracy
Color accuracy is another area where LED screens shine. LED technology allows for more precise control over how light is emitted, and this translates into a broader color range and more vivid, lifelike images. While LCD screens also produce good color accuracy, they often have a limited color range and can appear washed out compared to their LED counterparts.
Power Efficiency
LED screens are generally much more energy-efficient than traditional LCD screens. Since LEDs consume less power than fluorescent backlighting, LED screens use less electricity to produce the same level of brightness. This makes them more environmentally friendly and cost-effective in the long run. On the other hand, older LCD screens tend to consume more power due to their less efficient lighting systems.
| Feature | LED | LCD |
| Brightness/Contrast | + | - |
| Color Accuracy | + | - |
| Power Efficiency | + | - |
| Thinness/Design | + | - |
| Durability | + | - |
| Price | - | + |
Thinness and Design
LED screens are often thinner and more compact than traditional LCD screens. This is because LEDs are smaller and more efficient than the older fluorescent backlights. The ability to use edge-lit LEDs allows for ultra-thin designs, which is why many modern LED TVs, monitors, and laptops are incredibly slim. In contrast, traditional LCDs can be bulkier and less sleek in their design.
Durability
LED screens tend to have better durability and longevity compared to older LCD screens. Since LEDs are solid-state lighting devices, they have fewer components that can wear out over time. In comparison, older LCD screens can experience backlight failure, which significantly impacts the quality of the display. The more robust LED technology leads to a longer lifespan for the screen.
Price
Generally, LED screens can be more expensive than LCD screens due to the advanced technology involved in their construction. However, as LED technology becomes more widespread, the price gap has been narrowing, especially for entry-level models. While traditional LCDs may still be cheaper in certain cases, the additional cost of an LED screen is often justified by the improvements in performance and efficiency.
| Feature | LED Screens | LCD Screens |
| Brightness & Contrast | Significantly brighter; superior contrast ratios, deeper blacks. | Less bright; lower contrast ratios, grayer dark scenes. |
| Color Accuracy | Broader color range, more vivid and lifelike images. | Good color accuracy, but limited range, can appear washed out. |
| Power Efficiency | More energy-efficient, lower power consumption. | Less energy-efficient, higher power consumption. |
| Thinness & Design | Thinner and more compact, ultra-thin designs possible. | Bulkier and less sleek designs. |
| Durability | Better durability and longevity, fewer components to wear out. | Potentially shorter lifespan, backlight failure possible. |
| Price | Generally more expensive, but price gap narrowing. | Generally less expensive, especially older models. |
When comparing LED screens and LCD screens, it's important to look at how each technology performs across various applications, as they are both widely used but cater to different needs.
LED screens are highly sought after in applications where brightness, clarity, and color accuracy are paramount. They are ideal for digital signage, advertising billboards, and stadium scoreboards, where their ability to emit bright, vivid colors makes them stand out in direct sunlight or well-lit environments. These screens are also popular for TVs and monitors, especially in high-end models, where they offer superior contrast ratios, better color reproduction, and deeper blacks compared to traditional LCD screens. The energy efficiency and long lifespan of LED screens make them an ideal choice for commercial and outdoor settings, where the initial investment can be offset by the reduced maintenance and operating costs. Additionally, mobile devices, such as smartphones and tablets, benefit from LED screens due to their slim profile, low power consumption, and ability to produce vibrant colors, enhancing the user experience with high-resolution displays.
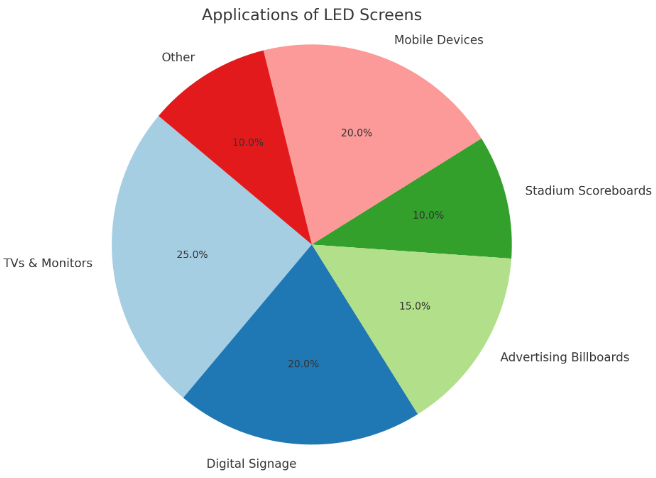
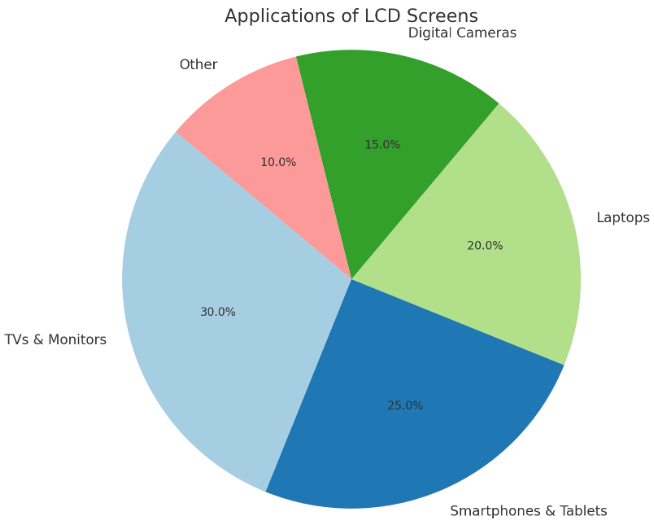
In contrast, LCD screens are often used in applications where cost-effectiveness and moderate image quality are prioritized. Smartphones, laptops, and TVs that are more budget-conscious typically utilize LCD screens, as they still offer solid performance but are less expensive to produce compared to LED displays. Although they don’t match the brightness levels of LED screens, modern LCDs can still deliver decent color accuracy and image sharpness, making them suitable for many general-use devices. Digital cameras, monitors, and projectors also often use LCD screens, especially when high resolution and color accuracy are important but the brightness of LED is not a critical factor. While LCD technology doesn't perform as well in bright environments and can struggle with producing deep blacks, it remains a popular choice for applications where affordability and basic visual quality are key, making it a dominant display technology for entry-level models in many consumer electronics.
While both LED and LCD screens can deliver excellent performance, LED is typically the superior choice in modern displays. The benefits of LED technology, including better brightness, higher contrast ratios, energy efficiency, thinner designs, and more accurate colors, make it the go-to option for most users. LED technology is more future-proof and offers a better viewing experience overall.
However, LCD screens may still be a viable option for those on a tight budget, as they can still provide a good viewing experience for basic tasks and entertainment. For users who prioritize image quality, color accuracy, and energy savings, LED is clearly the better option.